Barotropic Modes
Topographically trapped barotropic modes play a role in the adjustment of the ocean to variability in forcing (by the wind, mesoscale eddies, etc.), and are particularly important in the Southern Ocean; here the stratification is weak and bathymetry is pronounced, so the circulation is strongly steered by bathymetry. I use an eigenvalue solver to determine normal modes in a barotropic shallow-water model.
Our first investigations involved the intraseasonal oscillations in the Argentine Basin. Our normal mode analysis showed strong support for the hypothesis that the 20-25 day variability around Zapiola Rise, identified by Fu et al. (2001), is caused by a set of topographically-trapped barotropic modes (Weijer et al. 2007a; Weijer et al. 2007b).
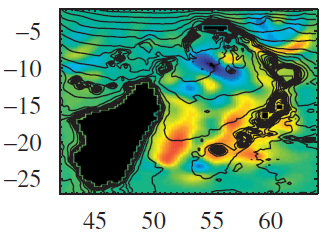
In Weijer (2008) I studied the normal modes of the Mascarene Basin, where a strong bimonthly signal was found in current meter data (Warren et al., 2002). My analysis showed that this variability is consistent with a barotropic normal mode of the Mascarene Basin, and can be described as an eigenmode of a basin tilted with respect to due north.
In Weijer et al. (2009) we studied the decay of topographically-trapped modes in the Australian-Antarctic Basin. We found the reason for the apparent discrepancy between the decay rate as observed from altimeters, and what can be expected based on frictional spin-down. We concluded that an arbitrary flow field has only a small projection on the mode; this component decays on the slow, frictional time scale. The remaining, unbalanced component, however, decays much faster (on the order of 3-4 days) as it disperses through Rossby waves. It is this rapid decay that dominates the SSH expression in altimeter data.
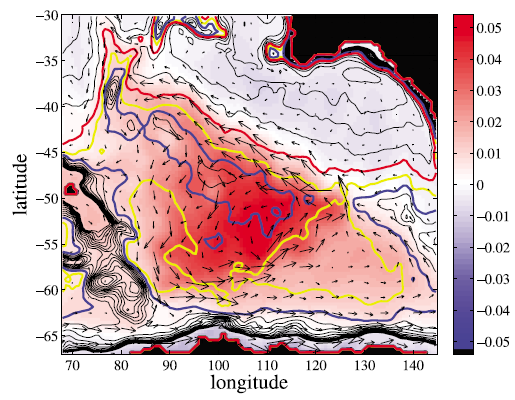
In Weijer (2010) I showed that most of the variability in the Australian-Antarctic Basin reflects stochastic excitation of an almost-free barotropic mode (Hughes et al. 1999); energy is trapped by contours of potential vorticity that are almost completely closed around the AAB. A bottleneck at the apex of the Wilkes Abyssal Plain appears to be crucial for the decay of the mode, as here energy is extracted from the mode and transferred to non-modal circulation (like waves).
In Weijer (2015) I followed up on this line of research by applying it to the Bellingshausen Basin. Observations (Boening et al. 2011) show an anomalously persistent circulation during the last quarter of 2009. Our analysis shows that this circulation reflects excitation of a topographically trapped barotropic mode. Interestingly, a similar event during the 3rd quarter of 2008 was more prominent from an energetics point of view, although its amplitude and persistence were weaker.
References
- Boening et al. 2011: A record-high ocean bottom pressure in the South Pacific observed by GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L04602.
- Fu et al. 2001: 25-Day Period Large-Scale Oscillations in the Argentine Basin Revealed by the TOPEX/Poseidon Altimeter. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 31, 506-517.
- Hughes et al. 1999: Wind-driven transport fluctuations through Drake Passage: a Southern Mode. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 29, 1971-1992.
- Warren et al. 2002: Forced resonant undulation in the deep Mascarene Basin. Deep-Sea Res. II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 49, 1513-1526.
- Weijer 2008: Normal Modes of the Mascarene Basin. Deep-Sea Research I, 55, 128-136, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2007.10.005.
- Weijer 2010: An almost-free barotropic mode in the Australian-Antarctic Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L10602, doi: 10.1029/2010GL042657.
- Weijer 2015: Modal variability in the Southeast Pacific Basin: Energetics of the 2009 event. Deep-Sea Res. II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 114, 3-11, doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.10.002.
- Weijer et al. 2007a: Multiple oscillatory modes of the Argentine Basin. Part I: Statistical analysis. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 37, 2855-2868, doi: 10.1175/2007jpo3527.1.
- Weijer et al. 2007b: Multiple oscillatory modes of the Argentine Basin. Part II: The spectral origin of basin modes. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 37, 2869-2881, doi: 10.1175/2007jpo3688.1.
- Weijer et al. 2009: Modal decay in the Australia-Antarctic Basin. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 39, 2893-2909, doi: 10.1175/2009jpo4209.1.


