|
SiAlON THIN FILM GROWTH & CHARACTERIZATION |
| Home About Research |
This
work focused on the development of silicon-aluminum oxynitride (SiAlON)
thin films to protect the surface of surface acoustic wave devices from
abrasion, corrosion, and oxidation. This particular type of thin
solid film was chosen because it has attractive mechanical and chemical
properties and can withstand very high temperatures which was a
requirement for the targeted application. The amorphous films
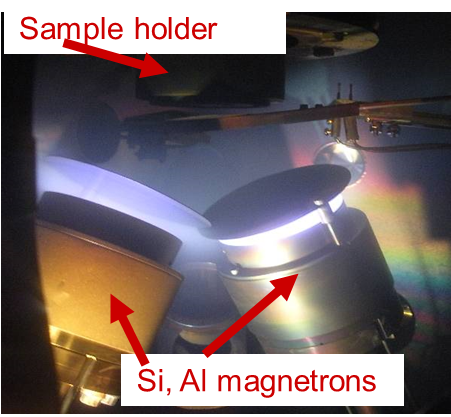
were grown by RF magnetron sputter of silicon and aluminum targets in
an argon-nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere. To achieve different film
stoichiometries, the power of the magnetrons, as well as the relative
concentration of the gases in the chamber, were systematically varied. Films with different growth parameters
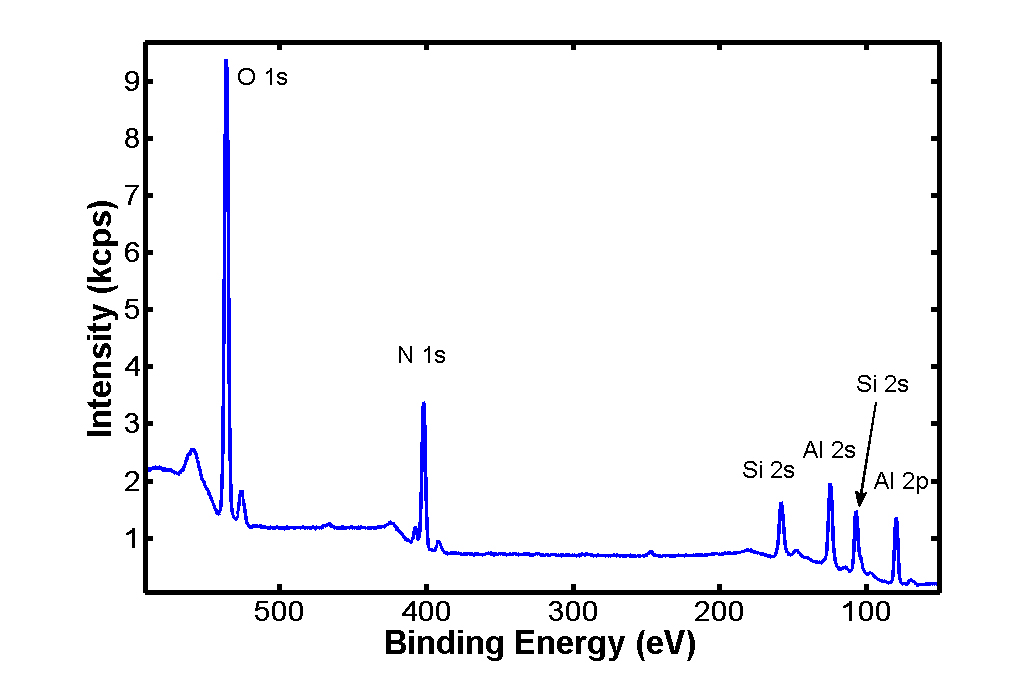
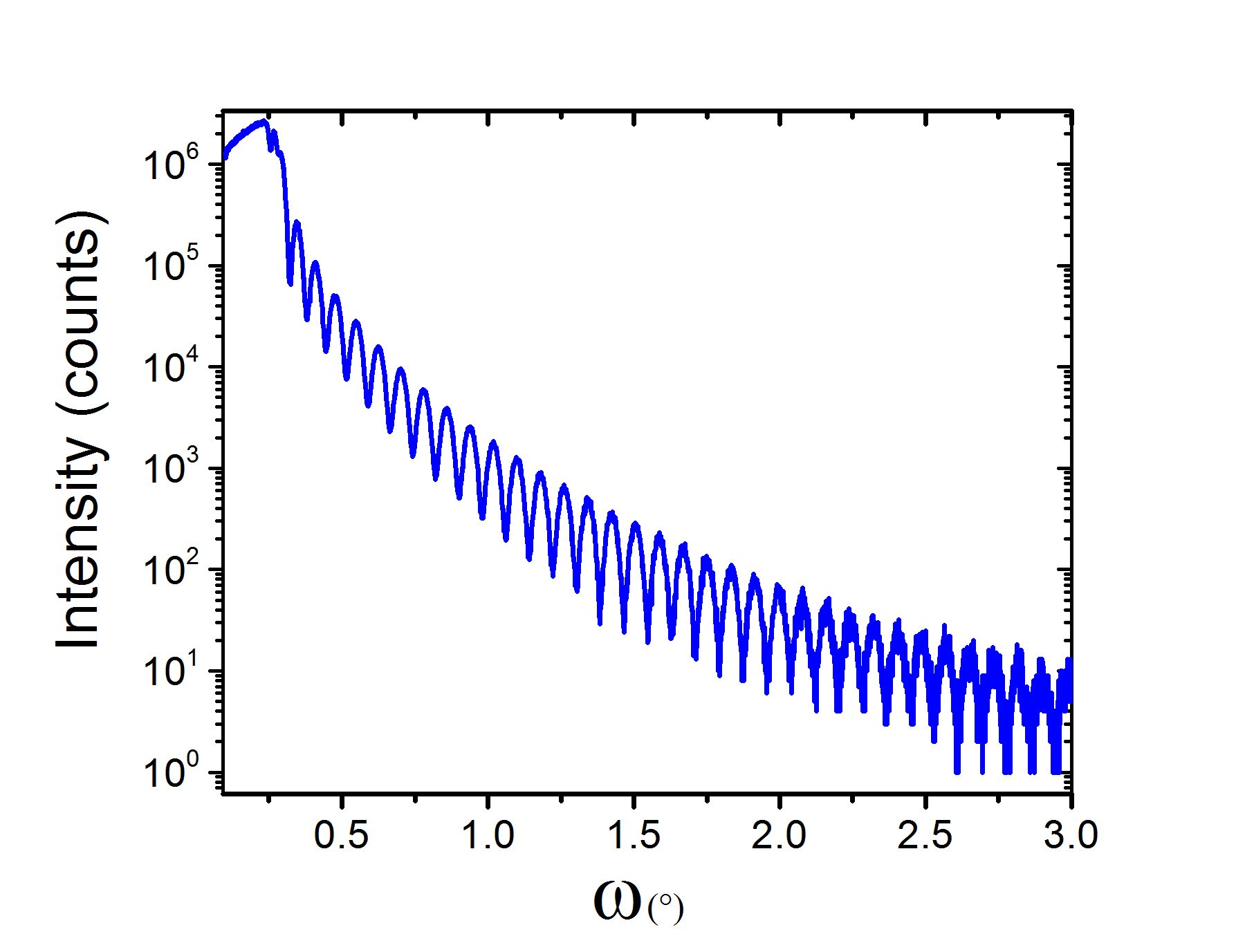
were characterized in terms of their hardness, chemical properties, and
structural properties. The images below show a few of the
techniques used to characterize the films. For more information about the growth and characterization of SiAlON films, please see these publications:
|
||||